NURS-FPX4030 Assessment 3 PICOT Questions and an Evidence-Based Approach Example PICO(T) Questions and an Evidence-Based Approach PICOT Question and Search Strategy Template Define your question using PICOT (review the “Create PICOT Questions” page as needed): Population: Patients who have experienced an acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
Place Your Order NowNURS-FPX4030 Assessment 3 PICOT Questions and an Evidence-Based Approach Example PICO(T) Questions and an Evidence-Based Approach PICOT Question and Search Strategy Template Define your question using PICOT (review the “Create PICOT Questions” page as needed): Population: Patients who have experienced an acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
NURS-FPX4030 Assessment 3 PICOT Questions and an Evidence-Based Approach Example
PICO(T) Questions and an Evidence-Based Approach
PICOT Question and Search Strategy Template
- Define your question using PICOT (review the “Create PICOT Questions” page as needed):
Population: Patients who have experienced an acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
Intervention: Implementing an evidence-based cardiac rehabilitation program.
Comparison: Compared to standard post-AMI care without cardiac rehabilitation
Outcome: Reducing the risk of future cardiovascular events and mortality
Time (optional): Over one year
- Write out your question:
For a patient who has had AMI, what is the effect of implementing an evidence-based cardiac rehabilitation program instead of standard care immediately after an AMI on the risk of future cardiovascular events and mortality over a year?
- Write down the most important words from your question in the gray boxes. For each top term, add synonyms or related terms in the boxes below it. All these are your search terms.
| Acute myocardial infarction | AMI | heart attack | cardiac rehabilitation |
| recurrent events | cardiovascular risk | secondary prevention | exercise rehabilitation |
| mortality |
- Review the “Best Bets” in the Nursing Databases list. Check the databases you will search:
- Nursing & Allied Health
- Public Health Database
- PubMed Central
- Write in your first search below. Follow the instructions on the “Find EBP Articles…” page.
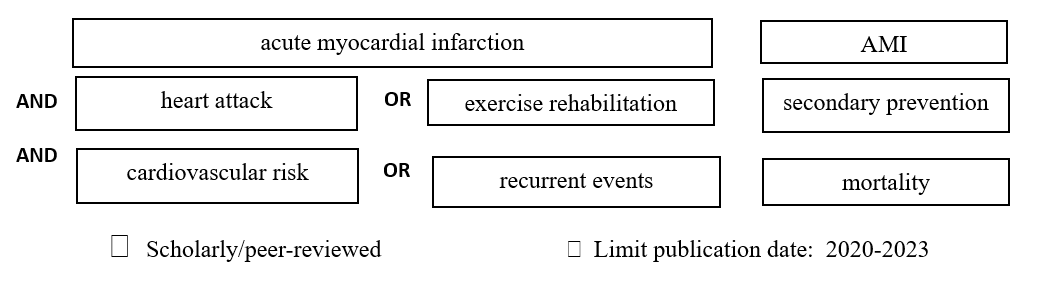
- Type of studies you want to include in your search:
- Systematic Review or Meta-Analysis
- Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Individual Research Studies
- What information did you find to help answer your question?
Two highly relevant sources were identified that provide good evidence to help answer this PICO(T) question:
Source 1:
Dibben, G., Faulkner, J., Oldridge, N., Rees, K., Thompson, D. R., Zwisler, A.-D., & Taylor, R. S. (2021). Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for coronary heart disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2021(11). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd001800.pub4
The present Cochrane systematic review was upgraded and included 85 randomized controlled trials with 23,430 participants with coronary heart disease, mostly having a myocardial infarction or revascularization procedure. The trials were designed to examine the effectiveness of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation programs, including some that had psychosocial or educational components as further additions, against control groups that received no exercise intervention (Dibben et al., 2021).
At the 6-12 months short-term follow-up, exercise-based cardiac rehab is most likely associated with a significant reduction of all-cause mortality, a large decrease in MI risk, and a need for hospitalization in individuals compared to the controls. The same results were probably observed regarding cardiovascular mortality, the need for CABG and PCI revascularization procedures, or cardiovascular hospitalizations.
At longer-term follow-ups, which reach three years, benefits may include a significant reduction in mortality caused by cardiovascular diseases and MI risk. Still, the evidence for the effect of revascularization needs to be more specific (Dibben et al., 2021). Cardiac rehab that ce
Order Now






